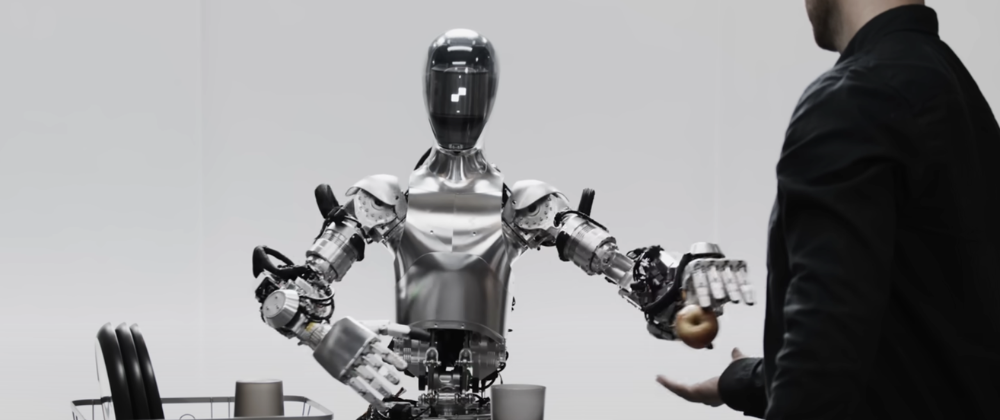
The field of humanoid robotics has seen a surge of investments and new startups in recent years, as companies and investors recognize the immense potential of this technology. One of the most notable examples is Figure AI, a startup founded just last year that has already raised a staggering $675 million in funding to accelerate the development of its first autonomous humanoid robot.
The funding round was led by an impressive list of tech giants, including Jeff Bezos through his firm Bezos Expeditions, Nvidia, OpenAI, Microsoft, and Amazon's Industrial Innovation Fund. This influx of capital, combined with Figure's partnership with OpenAI, is expected to significantly boost the company's efforts to commercialize its humanoid robots and bring them into real-world applications.
Figure's CEO, Brett Adcock, envisions deploying millions, or even billions, of humanoid robots to perform tasks that may be undesirable or unsafe for humans, particularly in light of labor shortages. The company's goal is to create robots that can replace the need for such jobs, allowing workers to "live happier, safer, and more purposeful lives."
In addition to Figure, there are several other prominent humanoid robot projects and startups emerging around the world:
- Ameca, developed by Engineered Arts in the UK, is known for its highly expressive and human-like face.
- Alter 3, created by Hiroshi Ishiguro Laboratories in Japan, is a humanoid robot designed for communication and interaction.
- ARMAR-6, developed by the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology in Germany, is a robot assistant designed to work alongside humans in industrial settings.
- Apollo, a collaboration between NASA and Apptronik, is a humanoid robot tailored for space exploration missions.
- Jiajia, created by the University of Science and Technology of China, is a female humanoid robot capable of natural conversation.
- RoboThespian, developed by Engineered Arts, is a humanoid robot designed for entertainment and public interaction.
- Sophia, created by Hanson Robotics, is a well-known humanoid robot that has gained fame for its ability to engage in conversation and express emotions.
- Surena IV, developed by the University of Tehran in Iran, is a humanoid robot capable of walking, grasping objects, and making facial expressions.
These projects and startups are pushing the boundaries of what is possible with humanoid robotics, from natural interaction and emotional expression to dexterity and navigation in complex environments. However, they still face significant challenges, such as overcoming the "uncanny valley" effect and ensuring safe and reliable operation in real-world settings.
Despite these challenges, the substantial investments and growing number of startups in the field suggest that humanoid robotics is poised for rapid growth in the coming years. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see more and more humanoid robots entering our workplaces, homes, and daily lives, potentially transforming the way we interact with machines and each other.






Top comments (0)